About Your ReportThrough FDA cleared Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA) technology, Tanita’s exclusive technology allows this monitor to not only measures weight and body fat, it also provides muscle mass, body water %, basal metabolic rate (BMR), metabolic age, bone mass, visceral fat and rates body physique! BIA is quick and non-invasive, and is one of the most thorough and reliable ways to measure body composition, clinically comparable to DXA (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) and hydrostatic (underwater) weighing. Fat % & Fat MassFat Mass is the weight of fat in your body. Fat % is the proportion of Fat to the total body weight. Body Fat is essential for maintaining body temperature, cushioning joints and protecting internal organs. Yet, too much fat can damage your health. Reducing excess levels of body fat has shown to reduce the risk of certain conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, type 2 diabetes and cancer. Too little body fat may lead to irregular periods in women and infertility. Check your body fat results against the healthy body fat ranges shown at the bottom of your printout. Fat Free Mass (FFM) Fat Free Mass is comprised of non-fat components of the human body. Muscle, bone and water are all examples of fat free mass. Body Mass Index (BMI)Body Mass Index is a standardized ratio of weight to height, and is used as a general indicator of health. Your BMI can be calculated by dividing your weight (in kilograms) by the square of your height (in meters)
BMI is a good general indicator for population studies but has serious limitations when used for individual analysis. |
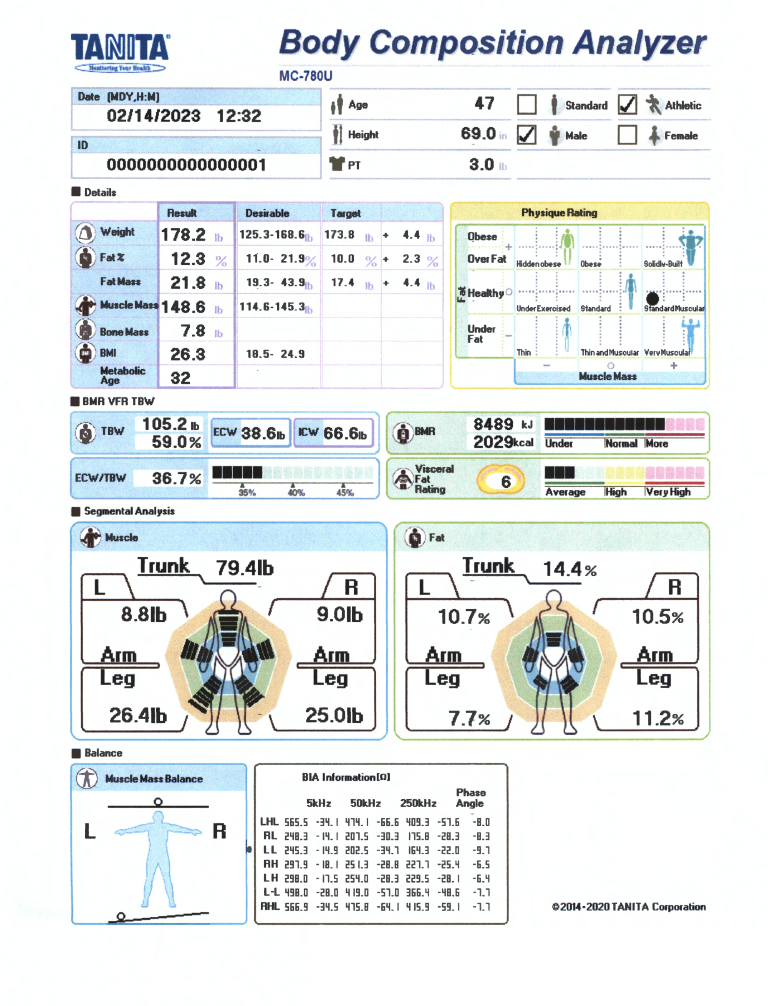
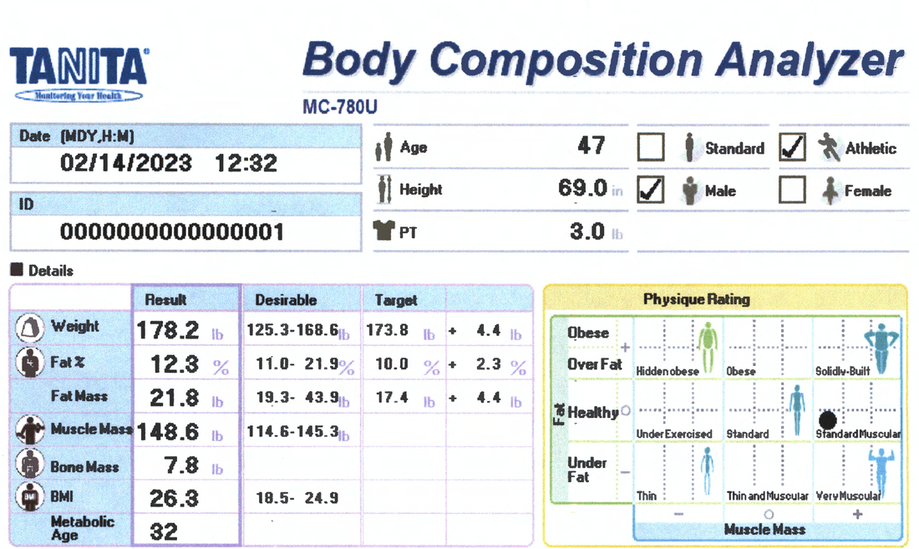
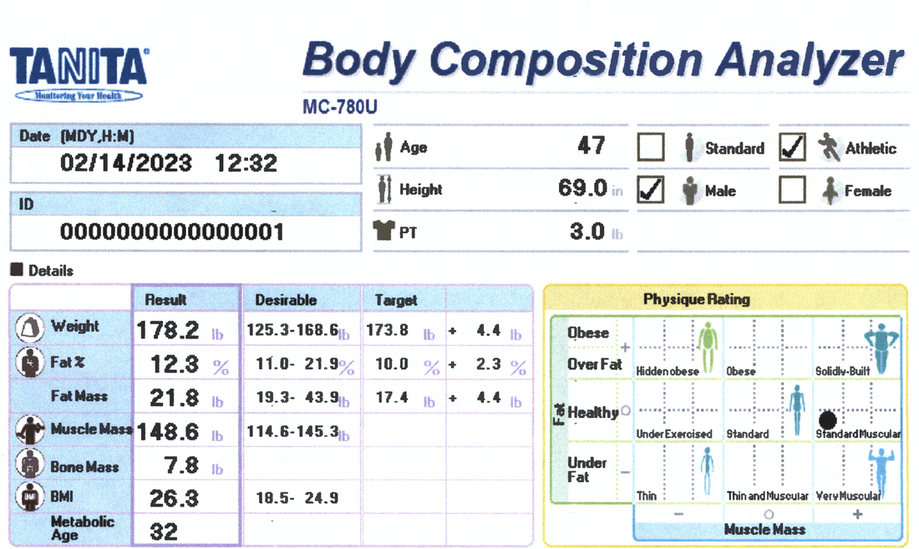
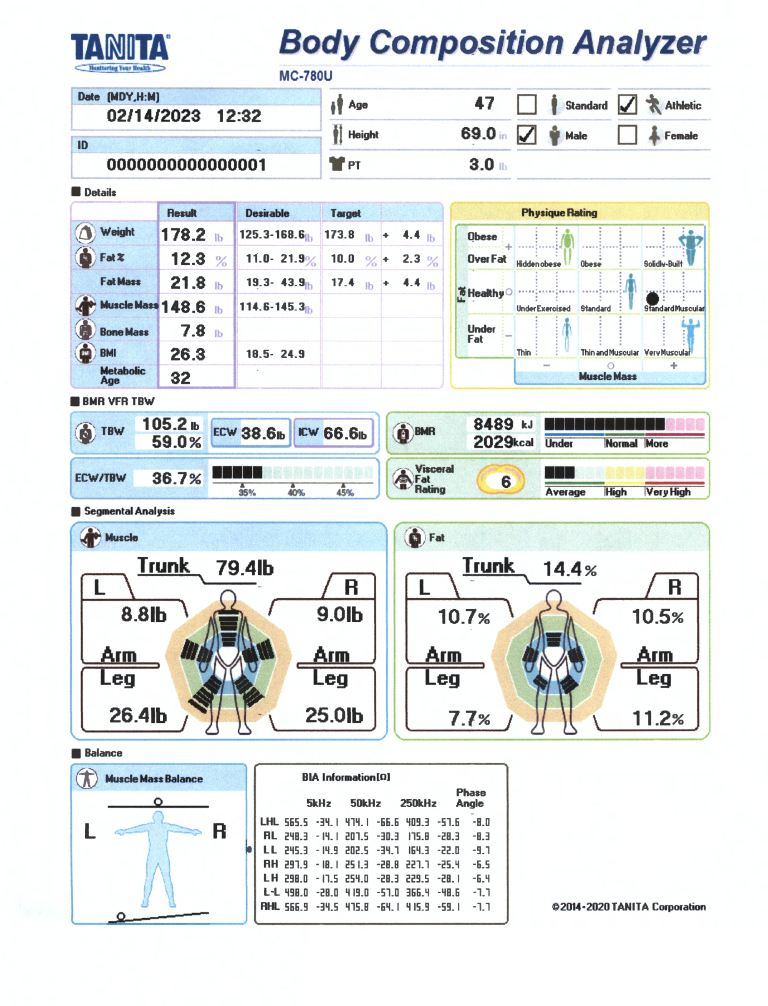
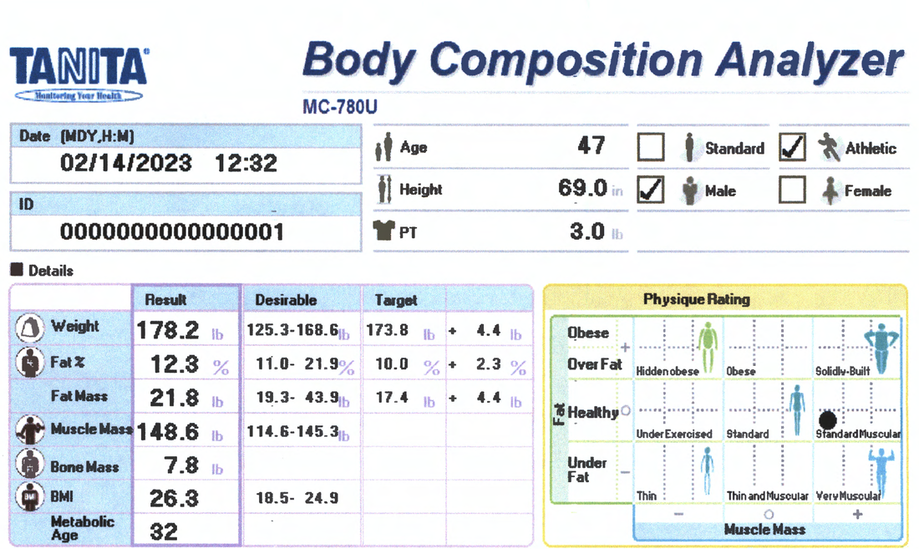
Body Composition Report
|
About Your Report
Through FDA cleared Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA) technology, Tanita’s exclusive technology allows this monitor to not only measures weight and body fat, it also provides muscle mass, body water %, basal metabolic rate (BMR), metabolic age, bone mass, visceral fat and rates body physique! BIA is quick and non-invasive, and is one of the most thorough and reliable ways to measure body composition, clinically comparable to DXA (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) and hydrostatic (underwater) weighing. |
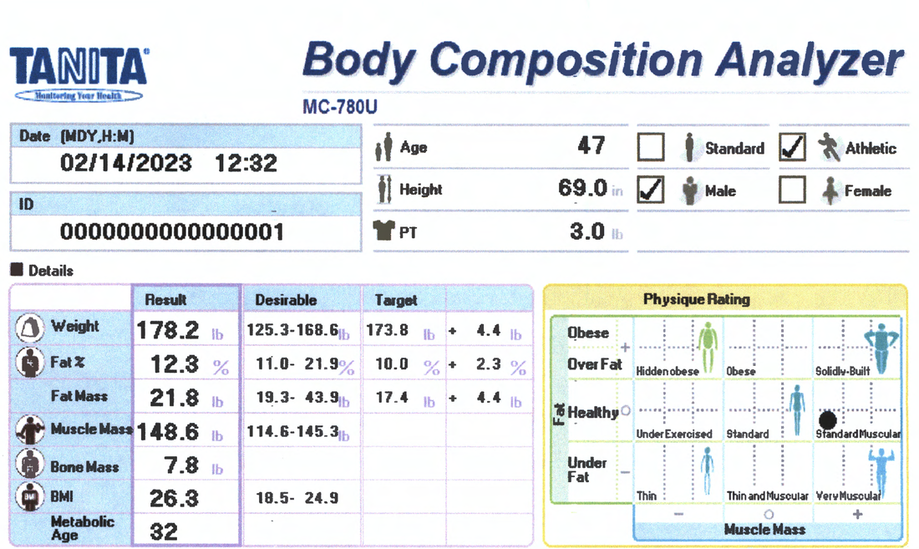
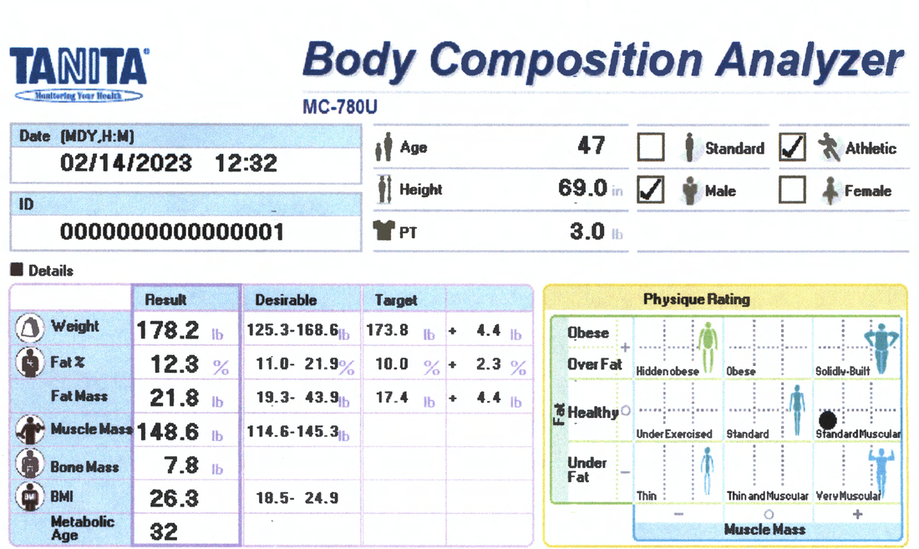
Body Composition Details
Fat % / Fat Mass
Fat Mass is the weight of fat in your body. Fat % is the proportion of Fat to the total body weight. Body Fat is essential for maintaining body temperature, cushioning joints and protecting internal organs. Yet, too much fat can damage your health. Reducing excess levels of body fat has shown to reduce the risk of certain conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, type 2 diabetes and cancer. Too little body fat may lead to irregular periods in women and infertility. Check your body fat results against the healthy body fat ranges shown at the bottom of your printout.
Fat Mass is the weight of fat in your body. Fat % is the proportion of Fat to the total body weight. Body Fat is essential for maintaining body temperature, cushioning joints and protecting internal organs. Yet, too much fat can damage your health. Reducing excess levels of body fat has shown to reduce the risk of certain conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, type 2 diabetes and cancer. Too little body fat may lead to irregular periods in women and infertility. Check your body fat results against the healthy body fat ranges shown at the bottom of your printout.
+
Too little body fat may lead to irregular periods in women and infertility. Check your body fat results against the healthy body fat ranges shown at the bottom of your printout.
Fat Free Mass (FFM):
Fat Free Mass is comprised of non-fat components of the human body. Muscle, bone and water are all examples of fat free mass.
Muscle Mass:
The predicted weight of muscle in your body. As you exercise more, your muscle mass increases, which in turn burns more calories. Check your muscle mass rating against the desirable range.
Bone Mass
The predicted weight of bone mineral in your body. It has been proven that increased muscle mass through sport activities promotes stronger healthier bones. Check for significant changes over time.
Body Mass index (BMI):
Body Mass Index is a standardized ratio of weight to height, and is used as a general indicator of health. Your BMI can be calculated by dividing your weight (in kilograms) by the square of your height (in meters) <18.5 = Under Weight 18.5 – 24.9 = Normal Weight 25-29.9 = Overweight 30> = Obese
BMI is a good general indicator for population studies but has serious limitations when used for individual analysis.
Metabolic Age:
Metabolic age compares the rate you burn calories with the average for people of the same age, and calculate your metabolic age based on that. Put simply, your metabolic age calculation gives you an idea of how old you are on the inside.
Physique Rating:
Physique rating assesses muscle and body fat rating into 9 body types. As your activity level changes over time the balance of body fat and muscle will gradually alter which in turn will change your overall physique.
Fat Free Mass (FFM):
Fat Free Mass is comprised of non-fat components of the human body. Muscle, bone and water are all examples of fat free mass.
Muscle Mass:
The predicted weight of muscle in your body. As you exercise more, your muscle mass increases, which in turn burns more calories. Check your muscle mass rating against the desirable range.
Bone Mass
The predicted weight of bone mineral in your body. It has been proven that increased muscle mass through sport activities promotes stronger healthier bones. Check for significant changes over time.
Body Mass index (BMI):
Body Mass Index is a standardized ratio of weight to height, and is used as a general indicator of health. Your BMI can be calculated by dividing your weight (in kilograms) by the square of your height (in meters) <18.5 = Under Weight 18.5 – 24.9 = Normal Weight 25-29.9 = Overweight 30> = Obese
BMI is a good general indicator for population studies but has serious limitations when used for individual analysis.
Metabolic Age:
Metabolic age compares the rate you burn calories with the average for people of the same age, and calculate your metabolic age based on that. Put simply, your metabolic age calculation gives you an idea of how old you are on the inside.
Physique Rating:
Physique rating assesses muscle and body fat rating into 9 body types. As your activity level changes over time the balance of body fat and muscle will gradually alter which in turn will change your overall physique.
Close
BMR / VFR / TBW
Total Body Water % (TBW %):
Total Body Water Percentage is the total amount of fluid in the body expressed as a % of total weight. Being well hydrated will help concentration levels, sports performance and general wellbeing. Drinking 2 liters of fluid a day will ensure good hydration levels.
Total Body Water Percentage is the total amount of fluid in the body expressed as a % of total weight. Being well hydrated will help concentration levels, sports performance and general wellbeing. Drinking 2 liters of fluid a day will ensure good hydration levels.
+
The average TBW% ranges for a healthy person are:
Individuals with a high body fat % may fall below the recommended body water percentage. As body fat is reduced over time the TBW% should gradually improve.
Extra Cellular Water (ECW):
Extracellular Water is the body fluid found outside of cells. The healthy ratio of Extra Cellular Water and Total Body Water is around 40%. In some cases malnutrition, aging and high fat levels may cause the ratio to be higher than 40%. Athletes tend to have a lower ratio of less than 36%. Continue to monitor this ratio on a regular basis.
Intra Cellular Water (ICW):
Intracellular Water is the fluid found inside cells. Usually 40% of your body weight is intracellular water.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR):
Basal Metabolic Rate is the daily minimum number of calories your body needs when at total rest. Increasing muscle mass will speed up your metabolic rate. A person with a high BMR can burn more calories at rest than a person with a low BMR. Check how efficient your body is at burning calories in the Indicator section of your print out
Visceral Fat Rating:
Visceral fat is located deep in the abdominal area surrounding and protecting the vital organs. Ensuring you have a low level of visceral fat reduces the risk of certain conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes.
- Female 45 to 60%
- Male 50 to 65%
Individuals with a high body fat % may fall below the recommended body water percentage. As body fat is reduced over time the TBW% should gradually improve.
Extra Cellular Water (ECW):
Extracellular Water is the body fluid found outside of cells. The healthy ratio of Extra Cellular Water and Total Body Water is around 40%. In some cases malnutrition, aging and high fat levels may cause the ratio to be higher than 40%. Athletes tend to have a lower ratio of less than 36%. Continue to monitor this ratio on a regular basis.
Intra Cellular Water (ICW):
Intracellular Water is the fluid found inside cells. Usually 40% of your body weight is intracellular water.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR):
Basal Metabolic Rate is the daily minimum number of calories your body needs when at total rest. Increasing muscle mass will speed up your metabolic rate. A person with a high BMR can burn more calories at rest than a person with a low BMR. Check how efficient your body is at burning calories in the Indicator section of your print out
- - = low burn - your body is slow at burning calories
- 0 = average burn - your body is efficient at burning calories
- + = high burn - your body is highly efficient at burning calories
Visceral Fat Rating:
Visceral fat is located deep in the abdominal area surrounding and protecting the vital organs. Ensuring you have a low level of visceral fat reduces the risk of certain conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes.
- Rating from 1 to 12: Indicates you have a healthy level of visceral fat. Monitor regularly to ensure your rating stays within this range.
- Rating from 13 to 59: Indicates you have an excess level of visceral fat. Consider making changes in your lifestyle possibly through diet changes and/or increasing exercise.
Close
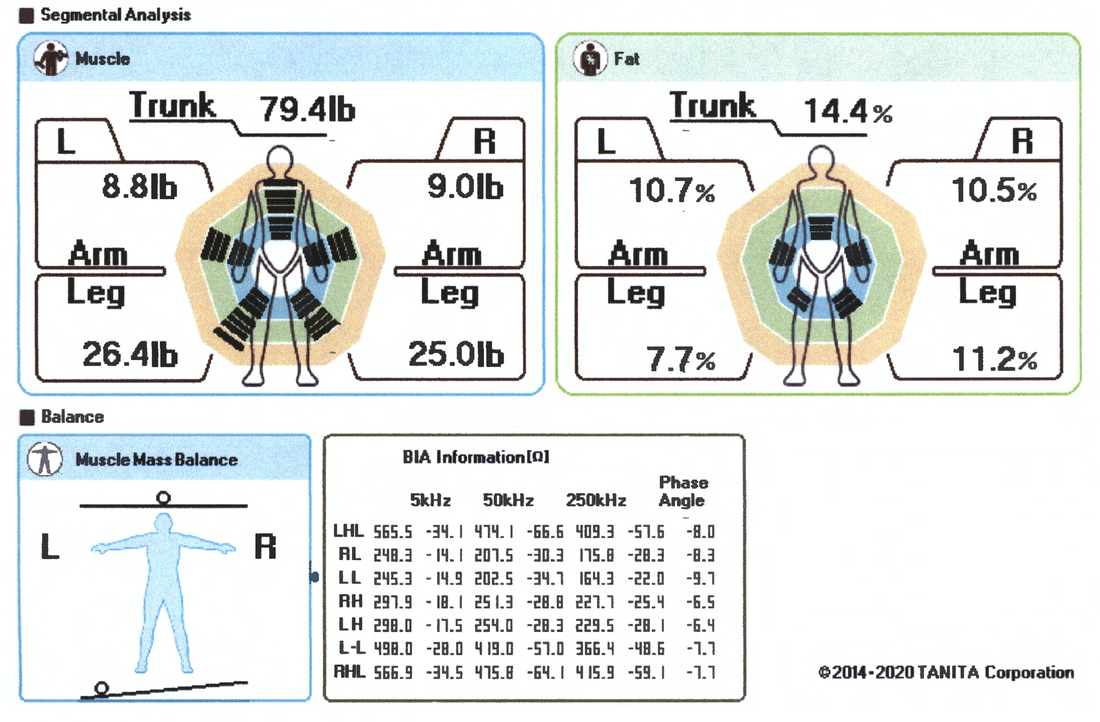
Segmental Analysis
Segmental Muscle Mass:
The shaded green area indicates the average person. The black line represents your muscle mass distribution. The muscle mass rating for the trunk, each leg and arm is shown:
The shaded green area indicates the average person. The black line represents your muscle mass distribution. The muscle mass rating for the trunk, each leg and arm is shown:
- Minus figures = low muscle tone
- Zero = healthy muscle tone
- Plus figures = high muscle tone
+
Ideally you should aim for Zero or plus figures to be healthy
Segmental Fat Rating:
The shaded green area indicates the average person. The black line represents your fat mass distribution. The fat mass for the trunk, each leg and each arm is shown:
Ideally you should aim for Zero or a little under to remain healthy
Muscle Mass Balance:
Compares the balance of muscle mass between the left and right side of the body.
Body Fat Distribution:
The ratio of upper to lower body fat is calculated, and plotted against average healthy values for gender and age.
Segmental Fat Rating:
The shaded green area indicates the average person. The black line represents your fat mass distribution. The fat mass for the trunk, each leg and each arm is shown:
- Minus figures = low fat level
- Zero = healthy fat level
- Plus figures = high fat level
Ideally you should aim for Zero or a little under to remain healthy
Muscle Mass Balance:
Compares the balance of muscle mass between the left and right side of the body.
Body Fat Distribution:
The ratio of upper to lower body fat is calculated, and plotted against average healthy values for gender and age.
Close